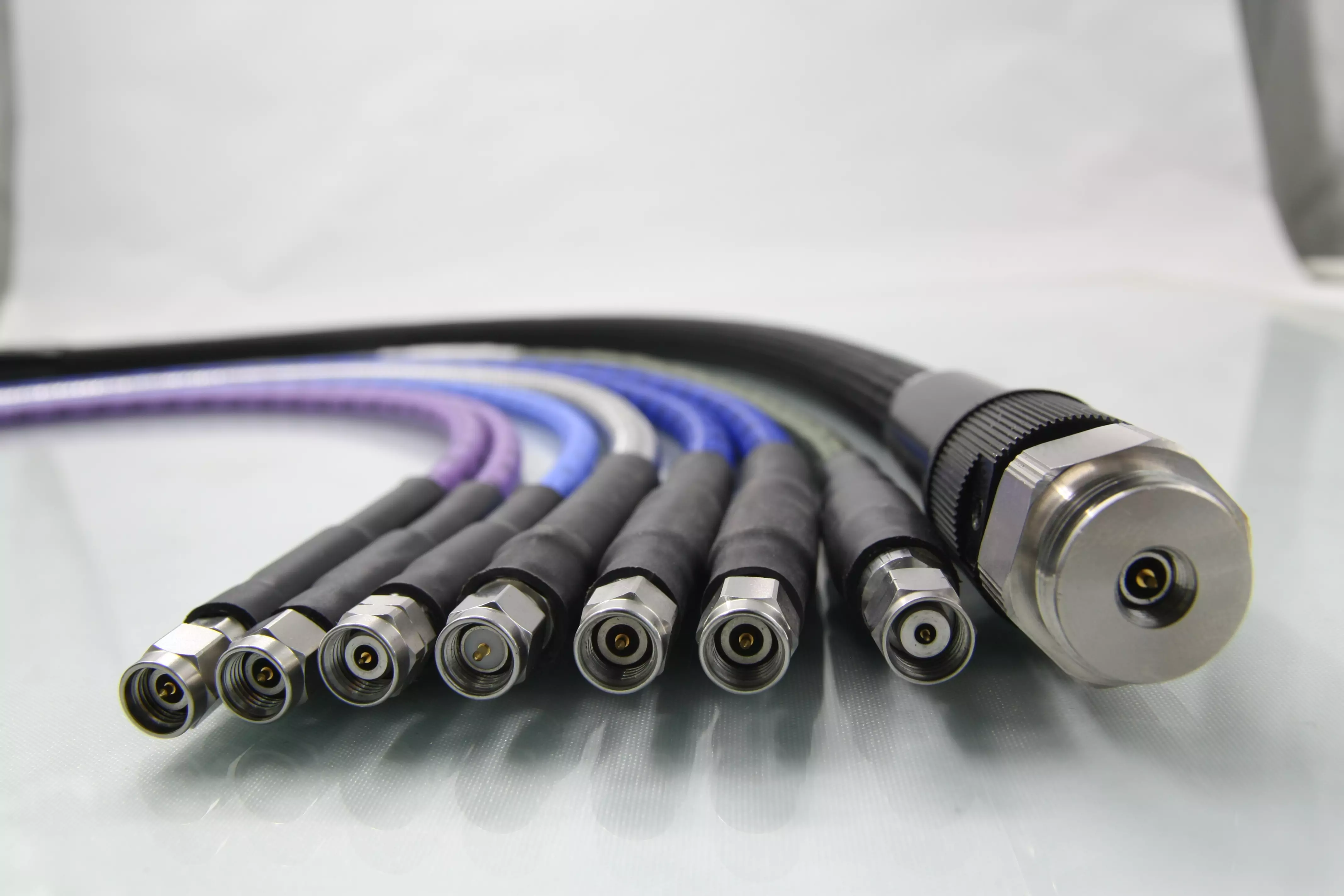
Key Differences Between Network Cables and Their Connectors
Networking is crucial to modern communication, enabling devices to interact and share information seamlessly. Understanding networking cables and their connectors is vital for anyone looking to delve into this field. Networking cables serve as the backbone of network infrastructure, while connectors play a critical role in establishing effective and reliable connections. This article will explore the key differences between network cables and their connectors, focusing on the fundamental aspects of networking, primarily the function of these cables and the various types available.
Understanding the Basics of Networking Cables
Networking cables are essential components used to connect devices within a network, facilitating communication and data transfer. The primary function of these cables is to transmit electrical signals or light signals between devices like computers, switches, routers, and other networking hardware. The effectiveness of a network largely depends on the quality and type of cable used, as improper cables can lead to data loss or transmission errors. Furthermore, selecting the right networking cable ensures compatibility with various devices, ultimately affecting network performance.
Major Types of Networking Cables
Ethernet Cables (Twisted Pair)
Ethernet cables, commonly known as twisted pair cables, are widely used in networking environments due to their cost-effectiveness and performance capabilities. These cables consist of multiple pairs of copper wires twisted together to minimize electromagnetic interference, thus enhancing signal quality. There are different categories of twisted pair cables, including Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a, each providing varying data transmission speeds and distances. When selecting an Ethernet cable, it is crucial to consider factors such as the required speed for specific applications and the network’s bandwidth demands.
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables utilize strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data in the form of light signals. This technology provides superior data transmission speeds and distance capabilities compared to traditional copper cables. Fiber optic cables are less prone to interference and signal degradation, making them ideal for high-bandwidth applications and long-distance connections. They are categorized into single-mode and multi-mode fibers, each having its own specific use cases depending on the network requirements. Understanding the advantages and limitations of fiber optic cables is essential for network engineers when designing and implementing network solutions.
Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables consist of a central conductor, insulating material, a metallic shield, and an outer insulating layer, which work collectively to transmit data. These cables are typically used for cable television and internet connections and are known for their durability and resistance to external interference. Coaxial cables are effective for short distances and can support high-frequency signals, making them suitable for certain networking applications. When considering coaxial cables, it is essential to evaluate their specifications to determine the appropriate use and ensure compatibility with the devices in the network.
RFecho is a company dedicated to revolutionizing networking solutions with cutting-edge technology and innovative products. We provide a comprehensive range of networking cables and connectors designed to deliver reliable performance and superior connectivity. Our team of experts pushes the boundaries of technology, ensuring that every product meets the highest industry standards. Experience seamless data transmission, enhanced network performance, and exceptional customer support with RFecho, your trusted partner in all your networking needs.
Exploring Different Types of Network Connectors
The Role of Network Connectors
Network connectors are essential components in the networking landscape, acting as the interfaces that join various networking cables to devices. These connectors facilitate the integrity of data transmission by ensuring a secure and reliable physical connection. Their designs can greatly influence a network’s performance, as the wrong type or poorly made connector may result in signal degradation, increased latency, and even complete network failure. A thorough understanding of selection criteria, such as compatibility with devices, environmental factors, and performance specifications, is critical for network engineers and IT professionals when implementing effective networking solutions.
Main Types of Network Connectors
RJ45 Connectors for Ethernet Cables
RJ45 connectors are one of the most common types of connectors used in Ethernet networking. These connectors are designed to work specifically with twisted pair cables, allowing for efficient data transfer within local area networks (LANs). The RJ45 connector includes eight pins, which align with the eight wires found within standard Category 5 (Cat5) and higher Ethernet cables. By properly crimping or terminating the cable with an RJ45 connector, network professionals can ensure a reliable connection with the capability of supporting high-speed data transmission at bandwidths of up to 1 Gbps or more, depending on the cable category utilized. Knowing the wiring standards, such as T568A and T568B, is also crucial when installing RJ45 connectors to avoid miswiring and potential network issues.
SC and LC Connectors for Fiber Optic Cables
SC (Subscriber Connector) and LC (Lucent Connector) connectors are widely employed in fiber optic networking. Both connectors allow for the effective transmission of data via light signals, making them suitable for high-speed and long-distance applications. The SC connector is a larger, push-pull design characterized by its durability, while the LC connector is smaller and more compact, allowing for higher port density in network panels. The performance of these connectors relies on the precise alignment of the optical fibers they connect, so optic professionals must pay attention to factors such as connector polish types and their impact on signal loss. Proper installation and maintenance of SC and LC connectors are vital for ensuring optimal network performance and minimizing troubleshooting complexities.
BNC Connectors for Coaxial Cables
BNC (Bayonet Neill-Concelman) connectors are commonly used in coaxial cable configurations, particularly in applications such as RF (radio frequency) transmission, video connections, and surveillance systems. These connectors provide a secure bayonet-style lock for ensuring a stable and reliable connection, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity. BNC connectors operate effectively with standard coaxial cables, and they can handle high-frequency signals necessary for various networking applications. Network technicians must be vigilant in selecting the appropriate size and type of BNC connectors that match the coaxial cable specifications to guarantee compatibility and performance. Regular inspection and proper handling of these connectors can help mitigate potential signal loss or disruptions in data transmission.
Comparative Analysis: Network Cables vs. Their Connectors
Fundamental Differences
The fundamental difference between network cables and connectors lies in their respective roles within a networking environment. Networking cables function as the primary medium for carrying data from one device to another, whereas connectors serve as the physical interfaces that effectuate the establishment of connections. Typically, cables are comprised of multiple conductors that facilitate either electrical or optical signal transmission, while connectors are engineered to terminate these cables, ensuring stable and reliable connections. Understanding this distinction is crucial, as each component’s functionality directly impacts the overall performance and reliability of the network.
Application Specifics
Performance in Various Scenarios
When evaluating network cables and their connectors, performance can vary significantly based on application specifications. In environments that demand high-speed connectivity—such as data centers or telecommunications—fiber optic cables paired with SC or LC connectors can outperform their twisted pair counterparts. Fiber optics not only provide enhanced bandwidth capabilities but can also extend signal reach without degradation, making them ideal for long-distance connections. Conversely, twisted pair cables and RJ45 connectors may suffice in local area networks (LANs) where slower data transfer rates are acceptable and cost-effectiveness is paramount.
In addition, the environmental conditions surrounding the installation also dictate performance differences. For instance, coaxial cables may be better suited for outdoor applications where invasive signals are common, as BNC connectors can withstand various weather conditions and are designed to minimize interference. On the other hand, indoor environments generally support the use of more specialized cabling and connectors that enhance aesthetic integration while maintaining network reliability. Understanding the specific performance capabilities based on these criteria is essential for industry professionals who aim to optimize network efficiency.
Cost Implications
Cost is another key factor that differentiates network cables from their respective connectors. Networking cables, depending on their type and specifications, can vary widely in price, particularly when considering the difference between copper and fiber optic options. For example, while twisted pair cables are generally more affordable, investments in fiber optic installations can yield higher upfront costs but often provide greater long-term advantages in terms of lower maintenance and operational expenses. When selecting cables, network professionals must balance both immediate budgeting constraints and the potential costs associated with future scalability and performance requirements.
In comparison, connectors also contribute to the overall cost of networking setups but tend to be less expensive than the cables themselves. However, the quality and type of connectors can also result in significant investments. For example, high-quality SC and LC connectors may have higher initial costs due to their precision engineering, but they may lead to fewer connectivity issues over time, and ultimately, reduced downtime. Thus, evaluating both connectors and cables as part of a total cost of ownership approach is vital for making well-informed purchasing decisions and maximizing network return on investment.
Practical Considerations for Choosing the Right Cable and Connector Combination
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in determining the appropriate cable and connector selection. For example, cables installed in areas with high exposure to electromagnetic interference may benefit from shielded twisted pair cables and connectors, thus reducing potential disruptions. Additionally, fiber optic installations require specialized handling and connectors that can account for bending and alignment to minimize signal loss. Networking professionals must consider these practical aspects, as neglecting them can lead to costly installation errors and prolonged repair times.
Lastly, ongoing maintenance and future scalability must not be overlooked during the selection process. High-quality cables and connectors can mitigate the need for frequent replacements or upgrades, potentially saving time and resources in long-term network management. Furthermore, planning for future expansion or increases in bandwidth can drive decisions on choosing specific cables and connectors. Ultimately, a strategic approach to selecting networking components will enable organizations to build resilient and efficient network infrastructures that can adapt to emerging technologies and trends.