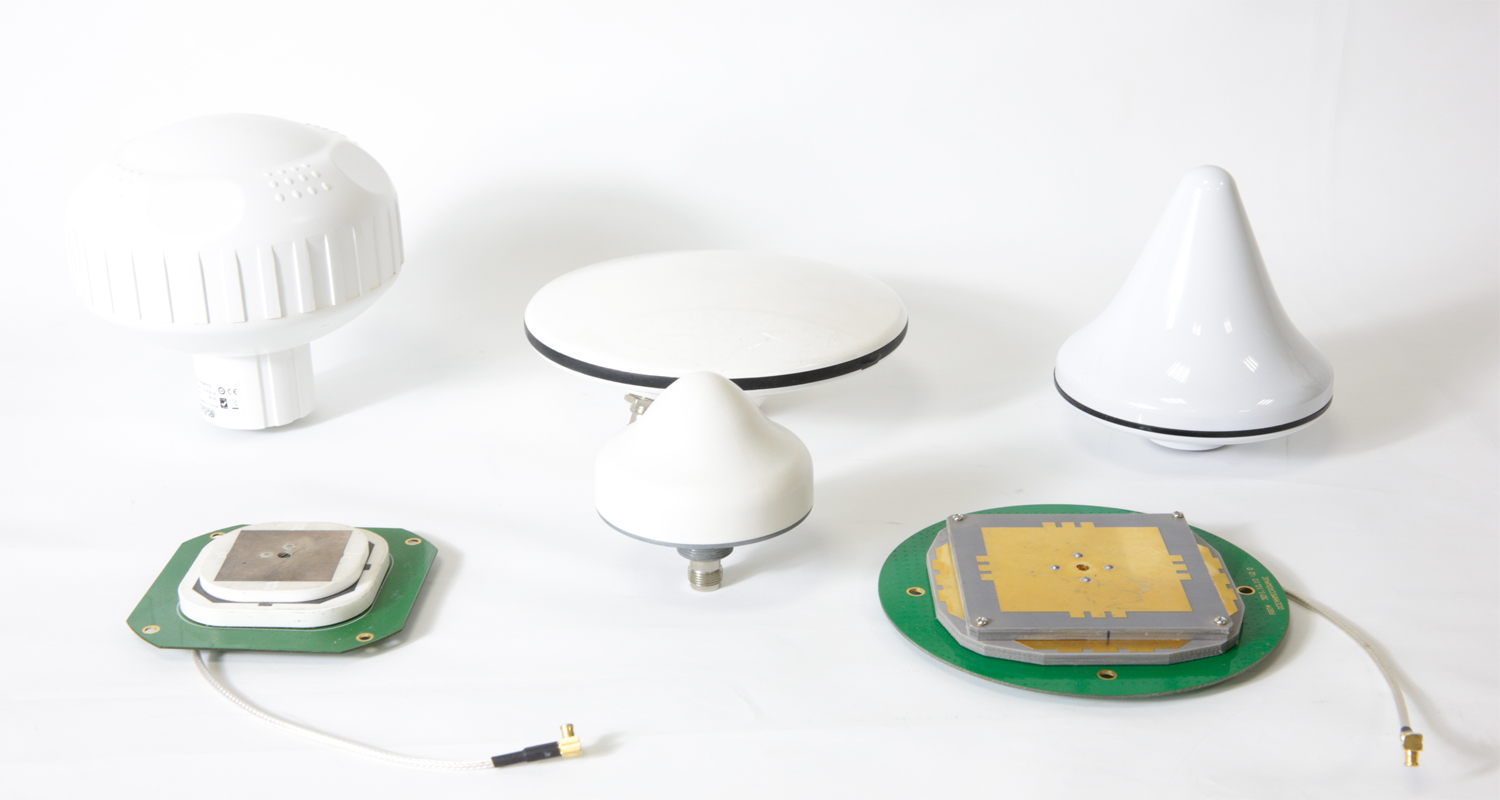
GPS Antenna
Satellite positioning systems, such as GPS, the European GALILEO, and the Russian GLONASS operate over disparate frequency bands. GPS employs Ll (1.575 GHz), L2 (1.227 GHz), and an additional frequency of 1.176 GHz for a new navigation signal; GALILEO uses frequencies: B1 (1.559 GHz-l.591 GHz), E5 (1.164 GHz-l.215 GHz), E6 (1.260 GHz-l.30 GHz) [1], [2] and the GLONASS uses 1.598 GHz-1.605 GHz. Hence multimode systems (GPS, GALILEO, and GLONASS) require coverage from 1.164 GHz to 1.610 GHz, which has a 446 MHz frequency range.
The global positioning system (GPS) is a wireless technology to access information from the satellite for navigation and tracking position. Today, its application is not only for the military but also for civilians. For civilian activities, the operating frequency of the GPS band. In the GPS system, the antenna is essential to transmitting and receiving the signal. Furthermore, in receiving system, the antenna requires a high gain to access the data from the satellite. Therefore, it can use the LNA to amplify the low signal for better quality. The specification of the GPS antenna depends on its implementation. For instance, GPS for a boat and automobiles do not require the dimension because of high signal demand and spacious places. When it comes to a mobile and portable device, the antenna’s smaller dimensions and shape are required.
An antenna that used active components integrated with a low-noise amplifier is called an active antenna. A micro-strip antenna and low noise amplifier (AILNA) are designed, then integrated into a single substrate for high gain and a more compact device to be applied for the GPS receiver. The design of the proposed antenna integrated with a low noise amplifier (AILNA) consists of a passive antenna and LNA design that can operate at frequencies at GPS application.
Keywords: GPS, RHCP, Compact GPS Antenna wideband unidirectional circularly polarized antenna
, GPS system
, Galileo system
, GLONASS system
, Global Positioning System